Architecture competition for care centre in Nyon, Switzerland
Client: Council of the Midi foundation
Team: Atelier mfmaarch
Mission: Concept Design for Social and mecial care centre
Total Floor Area: 4’330m2
Global cost:CHF.18'000'000.+ addtional design fees-- Excluding Taxes
Status: Competition
Year: 2015
Location: Nyon, Switzerland
Description:
Our project intends to pursue the social dimension of the social and medical care centre which allows to offer to aged people with the care needs in physical and psychological health situation for a certain period, a convivial space of living with cares for their material, affective and medical needs and to create the encounters of the socio-cultural activity.
Furthermore, it plans the spaces of «the apartment» in unity of living which receive and gather the local community spaces(animation spaces, cultural spaces, administration cafeteria/tea room and coiffure salon etc) within the accessible distance to all residents without the difficulty.
The softness and flexibility in the conjuring up of the accompanying concept will be obtained in the ways of use of the abundant and eco responsible materials and the design for the handicaped and the signage.
All these contribute to create the softness and flexibility and the intimate feeling of the reception and finally, give to persons received the feeling within more the apartment than the care centres.
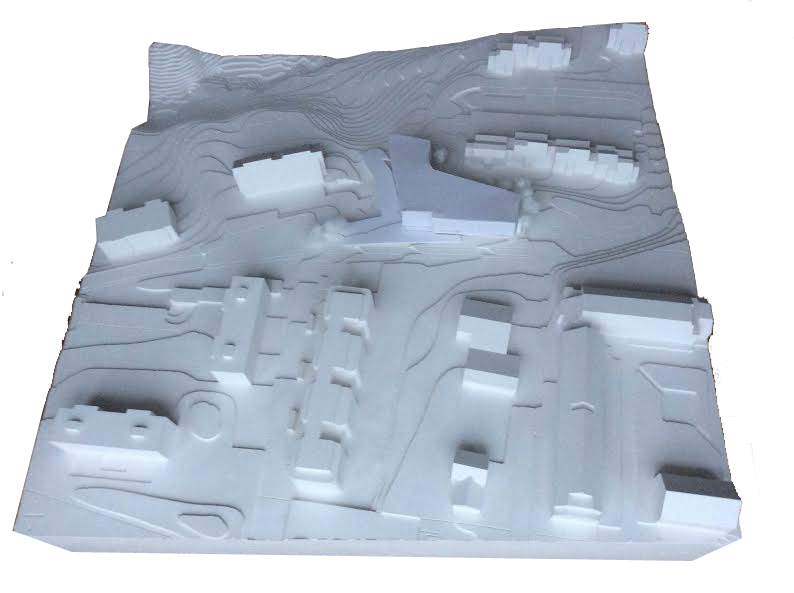
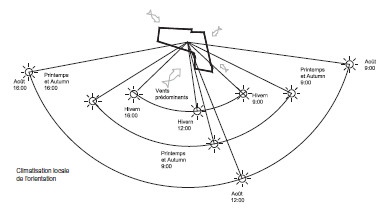
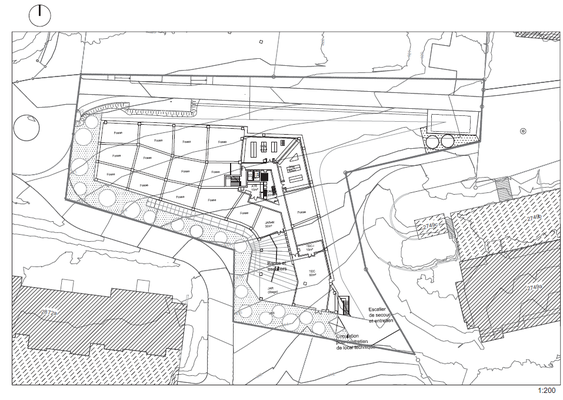
Site condition:Local climatization of the orientation
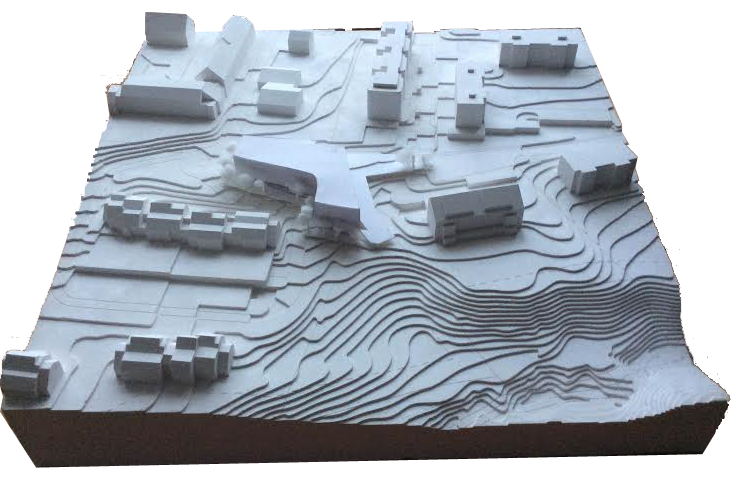
The site is a small district located near the léman lake and roughly half way between
Geneve and Lausanne and represents both historical and hilly or mountainous natural features.
The site organization is planned in consideration of the orientation.
The majority of the rooms is oriented towards the south and receive the exterior sun rays and the northern parts oriented to the north receive them from the north which is the source of the constant illumination during the day.
All the rooms face to the winds which increase the natural ventilation and supply the fresh air.
The trees in the southern parts block the strong and unpleasant winds in the front.
The toplights are located at the midst of the roofs for the intake of the natural lighting
within, which illuminates the circulation spaces.
Zone with the division about the pedestrians-cycling and cars-motor bikes:
In the site concerned, there is very clear division of the accessibility zones for
Pedestrians-Cycling and Cars-Scooters-Motor bikes in order to ensure the safety of the transport.
The access for basements and MEP rooms is planned in order to ensure easy exchange of equipment and to increase the life cycle of the building.
Zone accessible to vehicles for fire and emergence:
The routes for the users of the care centres in emergency are completely surrounded by the above zone and facilitate the access of the vehicles of pumps, fire and the emergence
in order to ensure the safety for the fire and the natural disaster like flooding.
Concept and the form generation:
The goal of the project over the course of the design is to put all programmes into
the perimeter area.
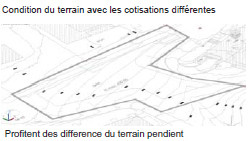
The site condition with the different contour lines leads to designing of benefiting well from the difference of the terrain inclination.
The site perimeter and its particular form can determine the urban condition such as the side for the built bloc and that for the roads which are detected by the building zone.
As a result, the volume defined and the space created by the terrain inclination emerge for the building.
As such, the relationship between the figure(building)-ground(site) is towards the figure assimilated to the ground and the ground. (Figure familiar with the ground-ground).
*Figure-ground theory is introduced by Collin Rowe, the author of the collage city and Peter Eisenman and mainly of urban design and urban morphology related to
the use of figure ground studies(wiki) which represents mass-void relationship and
the analysis of the urban fabric of relatively urbanized areas.
Also, it structures the primary urban landscaped elements as ground characteristics
to which landscape or natural elements of open spaces can be looked up.
As reference, those persons used the map of Roma and Roma interotta to explain figure-ground relationship or figure-figure urbanism etc.
References:
-Interview of Iman Ansari with Peter eisenman:Architecture review April 2013
-Figure-ground diagram by wiki
Characteristics of the interior
spaces of the building:
Zones for the circulation and divers courts and the access of rooms and the halls:
The use of the floor is optimized by the measurements taken in the present planning.
Those measurements are characterized in the following points.
1)Circulation is integrated into the divers halls border to border as a whole and created for the margins of two uses.
2)Divers halls not only hold their own functions but also play a role in connecting all rooms as the interior courtyard.
3)Routes and the access from rooms and halls are ensured through horizontal circulation and open with the clear visibility within the building.
The hall is well connected to the spaces and open within the building, all that gives the integration feeling.
Furthermore, each room is provided with the interior walls with the coloring signage to facilitate to residents the recognition of their rooms in unity.
The basement is half-reclaimed within the terrain and serve to be used as pits to conserve the waters and to manage all equipment which optimize the energy performance of the environmental service of the building.
A space created by the difference between the building and terrain is provided with banks in the form of the stairs with the stage and serve as that of recreation for residents and the people from the exterior who visit to the care centre.
All the surface of the landscape is covered with trees and grasses and connected to nearby forests and finally give to the site concerned quiet and pleasant environment.
The pits could be used for the purpose of the stockage of the rainwater and used waters for the recycling and the exhaust.
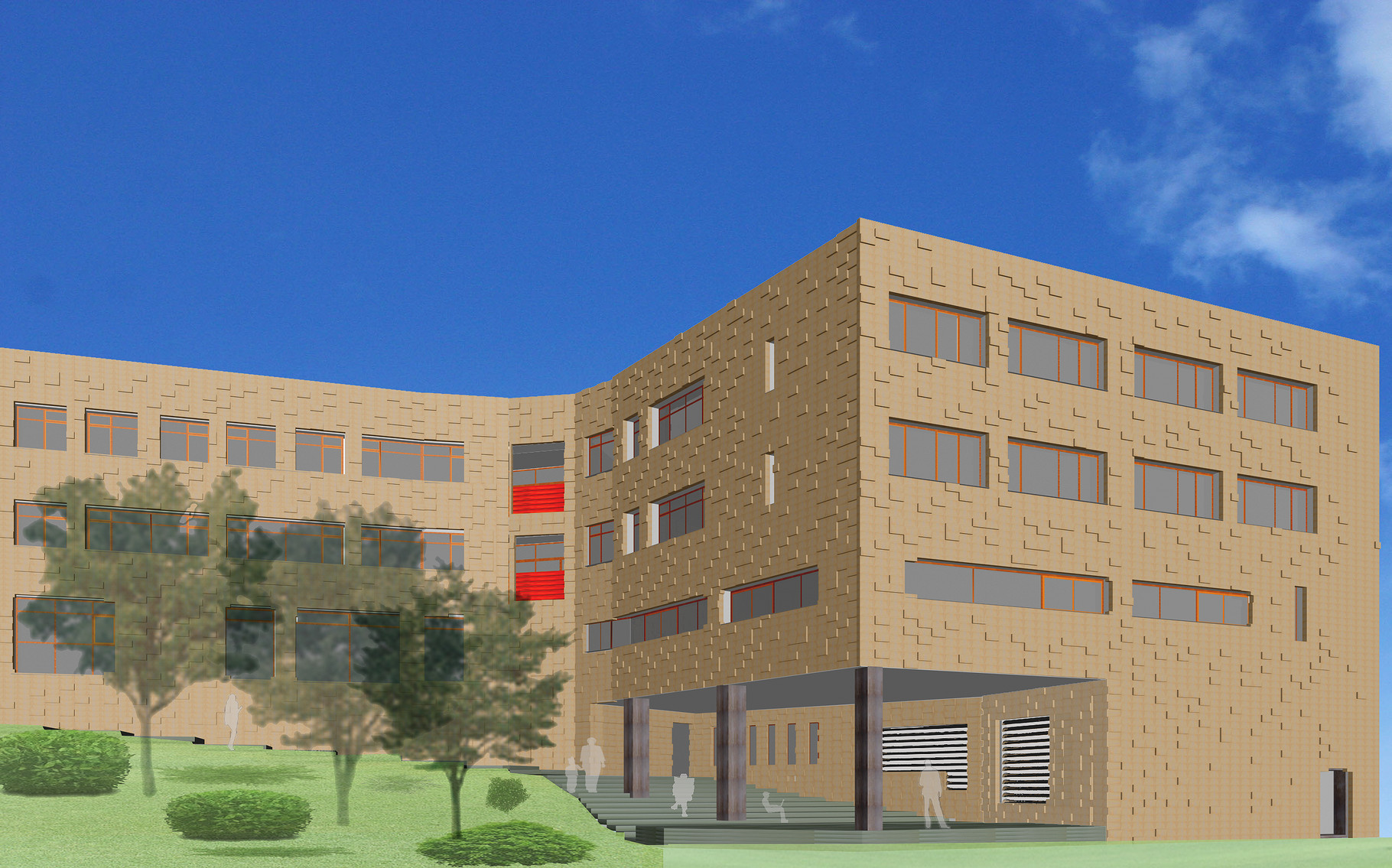
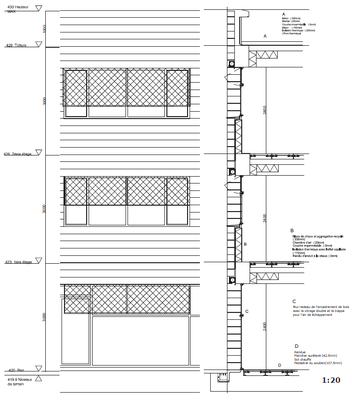
Exterior faces:
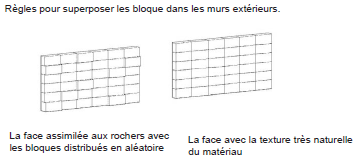
They are characterized by Eco limestone blocks which reduce drastically the environmental charge over the atmosphere and users of the building and by the rules to superpose the blocks on the exterior walls.
-The face resembled to rocks with the randomly distributed blocks.
-The face with very natural texture of the material.
All these measurements contribute to integrate the building whole within the context respecting the nature and existing terrain of the site in the soft way.
 atelier mfmaach
atelier mfmaach